
Using the Critical Path to Guarantee a Successful Shutdown
Shutdown, Turnaround, Outage are all the same thing. An extended planned downtime event, in which a tremendous amount of resources are utilized to ensure the site will be able to achieve its business goals. Whether the shutdown involves overhauls, CAPEX or a combination, the successful completion of the shutdown depends heavily on the planning and execution of it.
Shutdowns are resource intensive and often under compressed timelines. This unique situation requires a different approach to planning, scheduling and executing work, than the typically Maintenance Planning & Scheduling process.
By using the Critical Path Planning Process, shutdowns can be planned, scheduled, and executed with a high degree of predictability, resulting in an on time, on budget start up.
I remember the first time I had to plan a shutdown, it was uncoordinated, work was not scoped properly, and resources were overscheduled in certain areas. It was not a pretty sight. After that first shutdown I had to find a way to prevent that from happening again. After spending a bit of time looking, I stumbled across Critical Path Planning, a technique developed specifically for shutdowns.
My next shutdown resembled nothing like the first, and was completed on time, on budget, with minimum start up issues. The steps listed below will enable you to plan, schedule and execute a successful shutdown. The Critical Path Planning Process, is included in the steps below.
1. Pre Shutdown phase, can vary in length and start times depending on the industry you are in. It typically starts 16 – 26 weeks before the estimated shutdown start data. During the Pre-Shutdown phase a number of activities take place;
- A STO Coordinator is Appointed
- A Deadline is Established for New Work
- Define Success & Scope of the STO
- Notify Contractors
- Review Previous Learnings
- Establish the Critical Path
- Order Long Lead Time Materials
- Build in Time for Start-Up & Commissioning
- All Jobs are Properly Scoped & Planned
The Critical Path is established during this first phase. So what is the Critical Path, and how is it established?
The Critical Path Identifies the longest sequence of events, which cannot be delayed, without delaying the entire Shutdown. Establishing the critical path requires five steps;
- Specify the Individual Activities; Using a Unique Identifier List Out All Activities You Wish to Completed During the STO
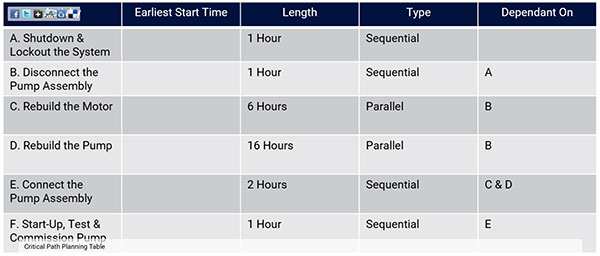
- Determine the Sequence of Activities; Determine Which Activities are Parallel or Sequential and which Activities they Are Dependant On
- Estimate Activity Completion Times; Using the Job Plans, Populate the Length of Time to Complete each Activity .
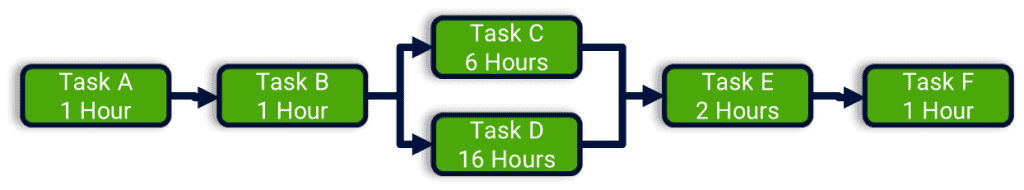
- Draw the Diagram; Using the Table, We Can Populate A CPM Diagram or Gantt Chart, Providing a Graphical View of the STO
- Using the Diagram, You Can Now Identify the Critical Path
2. Detailed Planning phase starts no later than 16 weeks from the shutdown start date. During the detailed planning phase, the following activities take place;
- Development of a Safety Plan
- Firm Dates Established (Start-Up / Shutdown)
- Schedule Developed, including Contractor Work
- Contingency Plans Developed
- Order Remaining Material
- Appoint Material Coordinator
- Prep Staging Areas
- Order Special Equipment
- Balance Resources Across the Site to Prevent Congestion
- Identify if additional resources are required (contractors)
- Identify which work can be dropped if “Emergency” work is discovered
- Review Contractor Job Plans
- Appoint Contractor Contacts
- Perform a Readiness Review with all functions and stakeholder.
3. Implementation; the day is here and the shutdown has started. If the process and activities above were followed, then you should be in great shape. However we still need to keep it on track. During this phase the following activities occur;
- Daily Review Meeting, which reviews;
- Work Status
- Safety Issues
- Material Issues
- Work Flow Upset
- Capture All Unanticipated Events
- Daily Safety Walks
4. Start-Up, is often one of the largest barriers to a successful shutdown. So what can you do to overcome the issues found during the start-up?
- Properly Planned Jobs
- Predefined Inspections of the Equipment w/ Operations
- Operations on Hand for Start-Up
- Continue Daily Meeting Until Site Reaches Full Performance
- Capture all Start-Up Issues for RCA
5. Post Shutdown phase is critical to the success of future shutdowns. During this phase you should;
- Evaluate the Shutdown & Determine Level of Success
- Review of all Issues & Successes. A SWOT analysis is ideal for this
- Perform RCA’s as Needed
- Implement Corrective Actions for the Next STO
- Review Contractor Performance on a 1 to 1 basis
- Track all Actions until completion
Planning for a successful shutdown is a tremendous amount of work, but when done properly, success is right around the corner.
How does the Critical Path Planning process differ from your existing shutdown planning process? What advantages do you see in using the Critical Path Planning process?
Remember, to find success, you must first solve the problem, then achieve the implementation of the solution, and finally sustain winning results.
I’m James Kovacevic
HP RELIABILITY
Solve, Achieve, Sustain
Leave a Reply